The Benefits and Risks of Self-Driving Cars is a hot topic that combines cutting-edge technology with everyday life. As autonomous vehicles edge closer to becoming a standard on our roads, it’s crucial to understand both the remarkable advantages they offer and the potential challenges they bring. From enhancing road safety to addressing ethical dilemmas, self-driving cars present a blend of opportunities and concerns that warrant thoughtful discussion.
Delving into the intricacies of self-driving car technology reveals a transformative evolution, with key industry players driving innovations aimed at making transportation safer and more efficient. These vehicles promise to reduce accidents, ease traffic congestion, and lower emissions, all while enhancing user convenience. However, with these benefits come significant risks, including technical failures, ethical quandaries, and cybersecurity threats that could redefine our approach to driving and transportation as a whole.
Overview of Self-Driving Cars
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, represent a significant leap forward in transportation technology. They utilize advanced technologies to navigate without human intervention, aiming to improve road safety, increase mobility, and transform urban planning. As this technology continues to evolve, it is essential to understand the underlying systems, historical developments, and major industry players driving this revolution.
Self-driving cars rely on a combination of various technologies, including sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence (AI). These components work together to perceive the vehicle’s surroundings, interpret data, and make real-time decisions. The backbone of this technology is machine learning algorithms, which allow the vehicle to learn from vast amounts of driving data, improving its performance over time. The operational framework includes different levels of automation, ranging from fully manual driving to fully autonomous systems capable of handling all driving tasks under any conditions.
Evolution of Autonomous Vehicle Development
The journey toward self-driving cars has been marked by significant milestones that illustrate technological advancements and regulatory changes. The evolution can be categorized into several key phases:
- Early Concepts and Research (1920s-1980s): The idea of automated vehicles dates back to the early 20th century, with initial explorations into radio-controlled cars and basic automation in the 1950s and 60s.
- First Autonomous Vehicles (1980s-2000s): Notable projects like the Carnegie Mellon University’s Navlab and the University of California, Berkeley’s Autonomous Land Vehicle project introduced basic self-driving capabilities, primarily in controlled environments.
- Commercial Interest and Advancements (2010s): Companies like Google launched ambitious projects, such as Waymo, testing vehicles in real-world scenarios, which led to significant advancements in AI and sensor technology.
- Regulatory and Market Readiness (2020s): The industry is witnessing increased regulatory engagement and partnerships with traditional automotive manufacturers, indicating a readiness for commercial deployment and acceptance of autonomous vehicles.
Key Players in the Self-Driving Car Industry
The self-driving car sector is competitive and comprises various stakeholders, each contributing to the development of autonomous technology. The industry features a mix of tech giants, automotive manufacturers, and startups:
- Waymo: As a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., Waymo is a pioneer in autonomous driving technology, focusing on ride-hailing services and testing its vehicles extensively on public roads.
- Tesla: Known for its innovative approach, Tesla integrates autonomous features in its electric vehicles through its Autopilot system, aiming for full self-driving capability.
- Ford: The automotive giant has invested heavily in self-driving technology, establishing partnerships and developing its Ford Autonomous Vehicles LLC to accelerate development.
- Uber: Despite challenges, Uber’s Advanced Technologies Group has been working on developing self-driving technology with the aim of integrating automation into its ride-hailing platform.
- Other Emerging Startups: Companies like Aurora, Cruise, and Zoox are also making strides in creating innovative solutions for autonomous driving, often with unique technologies and business models.
Benefits of Self-Driving Cars
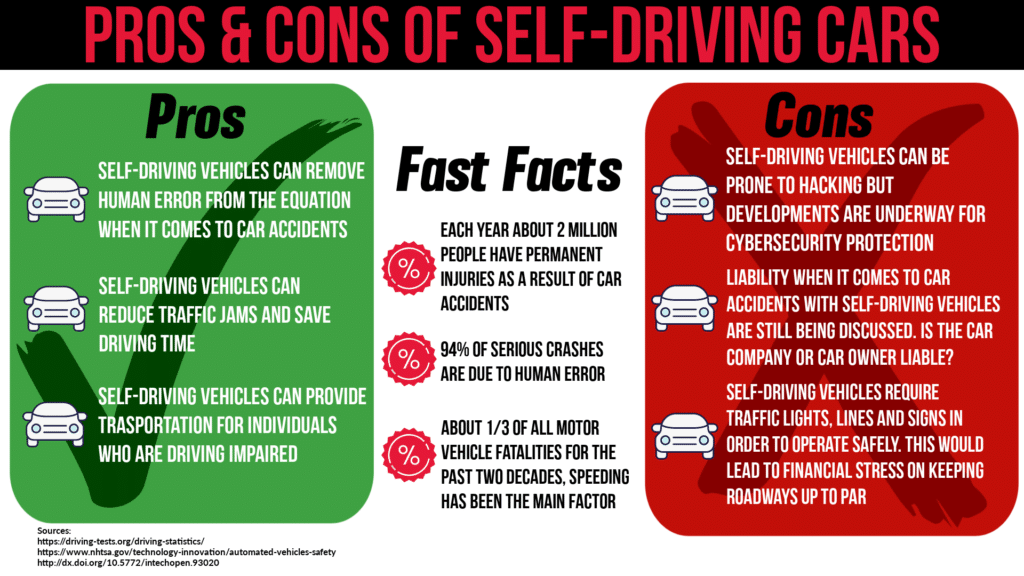
The emergence of self-driving cars presents a transformative shift in transportation, with numerous benefits that promise to redefine our driving experience, enhance road safety, and contribute positively to the environment. The integration of advanced technologies aims to create a future where vehicles operate autonomously, minimizing human error and optimizing travel efficiency.
Impact on Road Safety and Accident Reduction
One of the most significant advantages of self-driving cars is their potential to greatly enhance road safety. Human error is a leading cause of traffic accidents, accounting for approximately 94% of all crashes according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). By employing precise algorithms and real-time data analysis, self-driving cars can react to potential hazards faster than human drivers.
This technology can dramatically reduce accidents caused by distracted driving, speeding, and impaired driving.
“The automation of driving has the potential to save thousands of lives annually.”
For instance, Waymo, a leader in autonomous vehicle technology, has reported a notable decrease in accidents in areas where their self-driving taxis operate compared to traditional vehicles. As these technologies become more prevalent, the overall accident rate on roads could see a steep decline.
Improvement in Traffic Efficiency
Self-driving cars can significantly improve traffic efficiency, reducing congestion and optimizing travel routes. These vehicles can communicate with each other and with traffic management systems, allowing for more synchronized movement on the roads. This communication reduces stop-and-go traffic and helps maintain a steady flow of vehicles.The implementation of self-driving cars could lead to:
- Shorter travel times due to optimized routing.
- Fewer traffic jams through coordinated vehicle movement.
- Enhanced road capacity as autonomous vehicles can follow each other more closely.
Research from the Institute of Transportation Engineers indicates that smart vehicle technology could lead to a 20-30% reduction in travel time across major urban centers, showcasing a future where commuting becomes less of a hassle.
Environmental Benefits and Reduced Emissions
Another vital benefit of self-driving cars lies in their potential to positively impact the environment. By optimizing driving patterns and reducing unnecessary acceleration and braking, autonomous vehicles can achieve better fuel efficiency. This efficiency translates into lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to efforts against climate change.Self-driving electric vehicles (EVs) exemplify this environmental benefit. For instance, a study from the Union of Concerned Scientists found that EVs produce about 40% fewer emissions over their lifetime compared to conventional cars.
As more self-driving cars are designed as EVs, the cumulative impact on reducing carbon footprints can be substantial.
Convenience Aspects for Users
The convenience offered by self-driving cars significantly enhances user experience. With the ability to engage in other activities during transit, riders can reduce travel stress and make better use of their time. Passengers can catch up on work, relax, or even enjoy entertainment, transforming the commute into a more productive or enjoyable experience.Key conveniences include:
- Hands-free driving, allowing passengers to focus on other tasks.
- Accessibility features for individuals with disabilities who may have difficulty driving.
- On-demand transport options, eliminating the need for parking and reducing the hassle of finding a vehicle.
This shift not only enhances the quality of life but also fosters a culture of shared mobility, where car ownership is less about the vehicle itself and more about the seamless experiences it can provide.
Risks Associated with Self-Driving Cars: The Benefits And Risks Of Self-Driving Cars
The advent of self-driving cars brings a wave of excitement and optimism about the future of transportation. However, it is essential to recognize the significant risks that accompany this technological leap. From potential technical failures to ethical dilemmas and cybersecurity threats, understanding these risks is crucial for stakeholders, including manufacturers, regulators, and consumers.
Potential for Technical Malfunctions and Software Failures
Self-driving cars rely heavily on complex software algorithms and advanced hardware systems to navigate and make decisions. Although these technologies have advanced significantly, the potential for malfunctions remains a critical risk factor. For example, a software bug could lead to erroneous decision-making, causing accidents. High-profile incidents, such as the Uber self-driving car fatality in 2018, underscore the importance of rigorous testing and real-time monitoring of autonomous systems.
Continuous updates and system checks are necessary to mitigate risks associated with software failures, ensuring that self-driving vehicles operate safely under varying conditions.
Ethical Dilemmas in Decision-Making
The implementation of self-driving technology raises profound ethical questions, particularly in critical situations where harm is unavoidable. Autonomous vehicles must be programmed to make decisions that could directly impact human lives. For instance, in an unavoidable accident scenario, should the vehicle prioritize the safety of its occupants or pedestrians? These dilemmas present challenges for developers, who must consider how to encode ethical decision-making into algorithms.
Creating a standardized framework for addressing these ethical dilemmas is imperative to ensure public trust and safety.
Cybersecurity Threats to Autonomous Vehicles
As self-driving cars become increasingly interconnected, they also become susceptible to cybersecurity threats. Hacking incidents have the potential to compromise vehicle control systems, leading to dangerous outcomes. For instance, in 2015, researchers demonstrated the ability to remotely control a Jeep Cherokee, highlighting vulnerabilities in vehicle-to-network communication. To combat these threats, manufacturers must implement robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, regular software updates, and intrusion detection systems.
Building secure architectures is critical to safeguarding both vehicles and their passengers.
Implications on Employment in the Transportation Sector
The rise of self-driving cars poses significant implications for employment, particularly within the transportation sector. As autonomous vehicles become mainstream, jobs traditionally held by drivers—such as taxi, truck, and delivery drivers—may face substantial reduction. Estimates suggest that millions of driving jobs could be at risk, leading to economic and social challenges. For example, the American Trucking Associations has warned that up to 3.5 million truck driving jobs could be at stake due to automation.
Addressing the resulting unemployment will require innovative solutions, including retraining programs and policies to support those affected by this technological shift.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
As the technology behind self-driving cars rapidly advances, the need for appropriate regulations and legal frameworks becomes increasingly critical. Governments worldwide are tasked with ensuring that these vehicles operate safely while addressing the myriad of challenges that autonomous driving presents. Understanding the current regulatory landscape is essential for clear navigation of the self-driving vehicle market.Current regulations governing self-driving cars vary significantly across different countries and regions.
In the United States, regulations are primarily at the state level, with each state creating its own set of rules regarding testing and deployment. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has issued guidelines but lacks comprehensive federal laws governing the operation of autonomous vehicles. In contrast, countries like Germany have established more stringent regulations, requiring vehicles to meet specific safety standards before they can hit the roads.
Challenges in Formulating Laws Related to Autonomous Vehicles
The creation of effective laws for autonomous vehicles faces numerous challenges, primarily due to the technology’s complexity and rapid evolution. Policymakers must consider various factors, such as safety, ethical implications, and the need for innovation. Laws must be flexible enough to adapt to continuous technological advancements while also ensuring public safety. Several key challenges arise in this context:
- Balancing Innovation with Safety: Policymakers must find a way to encourage innovation in self-driving technologies without compromising public safety. The rapid pace of technological changes can outstrip the lawmaking process.
- Ethical Considerations: Autonomous vehicles may face situations requiring ethical decision-making during crashes. Establishing guidelines that dictate how these decisions are made is a complicated task.
- International Standardization: Different countries have varied standards and regulations, leading to confusion for manufacturers and users alike. An international consensus is necessary to streamline operations across borders.
Liability Issues in Accidents Involving Self-Driving Cars
Determining liability in accidents involving self-driving cars is a complex issue that lacks clear-cut answers. The question of who is responsible when an autonomous vehicle is involved in a collision can lead to contentious legal battles. Key considerations in liability issues include:
- Manufacturer Responsibility: If a self-driving car malfunctions due to software or hardware failure, the manufacturer may be held liable for damages, similar to traditional vehicle manufacturers.
- Owner’s Responsibility: If a vehicle owner has tampered with or failed to maintain their self-driving car properly, they may bear some responsibility for an accident.
- Software Developers: In cases where the vehicle’s AI makes a decision leading to an accident, the developers of that software could face liability claims.
The legal landscape surrounding self-driving cars is still evolving, highlighting the need for adaptable regulations and clear liability frameworks to ensure user safety while fostering innovation.
Public Perception and Acceptance
Public attitudes toward autonomous vehicles have undergone significant changes as technology has advanced. Initially met with skepticism, there is now a growing curiosity about the potential benefits of self-driving cars. Surveys indicate that while many individuals are still cautious, a substantial portion of the population is open to the idea of sharing the road with autonomous vehicles, especially when it comes to the promise of enhanced safety and convenience.
As people become more familiar with the technology, perceptions are gradually shifting, paving the way for acceptance.The media plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion regarding self-driving cars. Coverage of autonomous vehicle incidents can evoke strong emotional reactions, influencing how the public perceives the safety of these vehicles. Often, sensational headlines focusing on accidents can overshadow the vast amount of successful autonomous driving experiences.
This disparity in media representation leads to a polarized public view. To counter this, balanced reporting that highlights both the positive advancements and the challenges of self-driving technology is essential for fostering a more informed public discourse.
Strategies for Increasing Public Trust in Self-Driving Technology
Building public trust in autonomous vehicles is essential to encourage acceptance. Several strategies can be employed to boost confidence in this technology:
- Education and Awareness Programs: Initiatives aimed at educating the public about how self-driving cars work, their safety features, and the extensive testing they undergo can demystify the technology. Workshops, community events, and online resources can disseminate vital information.
- Transparency in Testing and Data Sharing: Companies should openly share data from tests and real-world deployments, including safety records and performance metrics. This transparency can help alleviate fears regarding reliability and safety.
- Collaboration with Authorities and Safety Organizations: Partnering with government bodies and safety organizations to create standardized guidelines and safety benchmarks can reinforce the commitment to safe autonomous driving.
- Promoting Positive User Experiences: Showcasing testimonials and success stories from individuals who have experienced self-driving technology can create a sense of familiarity and trust among potential users.
- Incremental Adoption: Gradually introducing autonomous features in conventional vehicles allows consumers to grow comfortable with the technology. Start with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that enhance safety and gradually progress to fully autonomous capabilities.
A multi-faceted approach combining education, transparency, collaboration, positive experiences, and gradual integration can significantly enhance public acceptance and trust in self-driving technology, ultimately leading to a safer and more efficient transportation landscape.
Future Trends in Self-Driving Technology
The evolution of self-driving cars is rapidly advancing, with numerous trends shaping the future of this technology. Innovations in various fields, particularly artificial intelligence and infrastructure, are anticipated to play a pivotal role in enhancing the capabilities and integration of autonomous vehicles. As we look ahead, it’s essential to identify key developments that will further influence the landscape of self-driving technology.
Upcoming Advancements in Self-Driving Car Technology
Significant advancements in self-driving technology are on the horizon, driven primarily by enhancements in sensor technology, machine learning algorithms, and connectivity.
- Improved Sensor Systems: Future self-driving cars will feature advanced sensor systems, including LiDAR, radar, and cameras that can detect and interpret a wider range of environmental conditions. This will improve visibility and reaction times in complex driving situations.
- Enhanced AI Algorithms: The development of more sophisticated artificial intelligence will allow vehicles to make real-time decisions with greater accuracy, incorporating vast volumes of data from various sources and improving safety and efficiency on the road.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: As connectivity improves, vehicles will be able to communicate with other cars, infrastructure, and even pedestrians. This will lead to better traffic management and accident prevention.
- Autonomous Fleet Services: Companies are likely to expand their fleets of autonomous vehicles for ride-hailing and logistics, increasing the availability of self-driving cars for everyday users.
Developments in Infrastructure to Support Autonomous Vehicles
The future of self-driving cars will not only rely on advancements in the vehicles themselves but also on significant improvements in infrastructure. Smart infrastructure will be essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of autonomous vehicles.
- Smart Traffic Signals: Integration of smart traffic signals that can adapt to real-time traffic conditions will facilitate smoother traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Dedicated Lanes for Autonomous Vehicles: The development of dedicated lanes for self-driving cars can enhance safety and efficiency, allowing these vehicles to operate more reliably without interference from human drivers.
- Charging Infrastructure: As electric self-driving vehicles become more prevalent, a robust network of charging stations will be critical to support their operation, especially in urban areas.
- Data-Driven Urban Planning: Cities will need to incorporate data analytics into their planning processes, ensuring that roadways and public spaces are designed with autonomous vehicles in mind.
Artificial Intelligence Enhancing Self-Driving Capabilities
Artificial intelligence is set to transform self-driving technology, making vehicles smarter and more responsive. The integration of AI not only improves vehicle autonomy but also enhances the overall user experience.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze patterns in traffic and driving behavior, enabling vehicles to anticipate and react to potential obstacles or changes in road conditions.
- Machine Learning for Continuous Improvement: Self-driving cars will utilize machine learning to continuously improve their algorithms based on real-world driving experiences, leading to safer and more efficient operations.
- Personalization Features: AI will allow vehicles to learn driver preferences, adjusting settings for comfort and convenience, which will make the experience of using self-driving cars more enjoyable.
- Advanced Safety Features: AI will enhance safety features, such as automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assistance, further reducing the likelihood of accidents and improving passenger safety.
Case Studies of Self-Driving Cars
The journey towards fully autonomous vehicles has been marked by both successes and setbacks. This section explores significant case studies that highlight various trials and deployments of self-driving technology, showcasing the diverse approaches taken by different companies in this rapidly evolving field.
Successful Trials and Deployments
Several companies have successfully tested their self-driving vehicles in real-world scenarios, demonstrating the potential of this technology. Notable examples include:
- Waymo: Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., has conducted extensive testing in Phoenix, Arizona, where its autonomous minivans operate without a human driver. The Waymo One service, launched in December 2018, allows users to hail rides in self-driving cars, showcasing a practical implementation of this technology.
- Tesla: Tesla’s Autopilot feature includes semi-autonomous capabilities that have been continuously updated through over-the-air software improvements. The company’s vehicles have accumulated millions of miles in real-world driving conditions, reflecting the effectiveness of their approach.
- Cruise: Cruise, owned by General Motors, has been testing its self-driving cars in San Francisco. In June 2022, the company received approval to operate its autonomous vehicles at night, marking a major milestone in urban self-driving applications.
Failures and Accidents
While there have been successes in autonomous driving, the technology has also faced significant challenges, including accidents and failures that have raised safety concerns. Key incidents include:
- Uber: In March 2018, an Uber self-driving vehicle struck and killed a pedestrian in Tempe, Arizona. This tragic incident led to a temporary halt of Uber’s autonomous vehicle testing and prompted widespread scrutiny regarding safety protocols in self-driving technology.
- Tesla: Several accidents involving Tesla vehicles operating on Autopilot have resulted in fatalities. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) launched investigations into these incidents, highlighting the importance of effective monitoring and regulation of autonomous systems.
Comparative Approaches to Development, The Benefits and Risks of Self-Driving Cars
Different companies have adopted varied strategies in the development of self-driving technology, influenced by their unique corporate philosophies and technological capabilities. The following points illustrate these diverse approaches:
- Data Utilization: Companies like Waymo leverage vast amounts of data collected from their vehicles to enhance their algorithms and improve safety features. This data-driven approach helps in fine-tuning the vehicle’s decision-making processes.
- Partnerships: Many firms, such as Aurora, have chosen to partner with automotive manufacturers to integrate self-driving systems into existing vehicle platforms, allowing for a more collaborative approach to development.
- Testing Environments: Some companies, like Cruise, focus on urban environments, while others, like Waymo, have expanded their testing to suburban areas, providing insights into how self-driving cars can adapt to different driving conditions.
“The development of self-driving cars requires not only technological innovation but also a deep understanding of the regulatory landscape and public perception.”





